

Severity: 8192
Message: Creation of dynamic property CI_URI::$config is deprecated
Filename: core/URI.php
Line Number: 201
Backtrace:
File: /home/jxlutxhi/public_html/index.php
Line: 962
Function: require_once

The financial landscape in Nigeria has witnessed a paradigm shift with the emergence and rapid adoption of peer-to-peer (P2P) platforms. These platforms have revolutionized the way Nigerians conduct financial transactions, offering a decentralized, fast, and cost-effective alternative to traditional banking systems. Initially, P2P platforms gained prominence through cryptocurrency trading, but their use has expanded to include remittances, cross-border payments, and even lending.
As the Nigerian economy grapples with challenges such as inflation, exchange rate volatility, and stringent financial regulations, P2P platforms have provided individuals and small businesses with greater financial flexibility. However, as the popularity of P2P platforms grows, an important question arises: Do these platforms primarily benefit the Nigerian people, or do they serve the interests of the government?
This comprehensive article explores the evolution of P2P platforms in Nigeria, their impact on the economy, the benefits and risks they pose to users, and whether they align more with the interests of the people or the government.
P2P platforms facilitate direct transactions between individuals or businesses without the need for intermediaries such as banks or financial institutions. These platforms leverage blockchain technology, smart contracts, and decentralized systems to ensure secure and transparent transactions.


P2P platforms have evolved significantly over the past decade, with multiple factors contributing to their growth and widespread adoption.


P2P platforms gained traction in Nigeria through cryptocurrency trading, where individuals and businesses sought alternatives to the official banking system. Platforms such as Binance P2P, Paxful, and LocalBitcoins allowed Nigerians to buy and sell cryptocurrencies using fiat currency, bypassing the restrictions imposed by the Central Bank of Nigeria (CBN) on cryptocurrency transactions.
As cryptocurrency adoption increased, Nigerians realized the potential of P2P platforms beyond crypto trading. This marked the beginning of a broader application of P2P systems in facilitating remittances, payments, and credit access.

Nigeria is one of the largest recipients of diaspora remittances in Africa, with inflows exceeding $20 billion annually. However, traditional remittance channels, including commercial banks and money transfer operators (MTOs), often charge high fees and take days to process transactions.
P2P platforms have disrupted this space by offering faster, cheaper, and more convenient remittance options. Nigerians can now receive funds from abroad in local currency through P2P networks at lower fees, reducing the financial burden on recipients and increasing the volume of remittances.


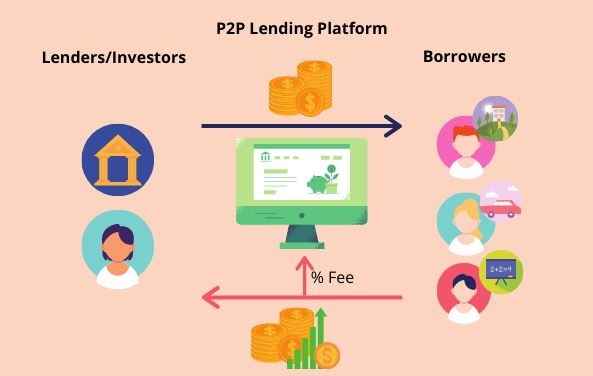
As financial inclusion became a priority for the Nigerian government, P2P lending platforms emerged to address the credit gap faced by small businesses and individuals. Platforms such as KiaKia, FINT, and Renmoney allow borrowers to access microloans from individual investors without traditional bank collateral.
These platforms democratize credit access, allowing unbanked and underbanked Nigerians to secure funds for business growth, education, and emergencies.
P2P platforms have undeniably transformed financial access and empowered millions of Nigerians by offering a decentralized alternative to traditional banking systems. Below are some of the key benefits:
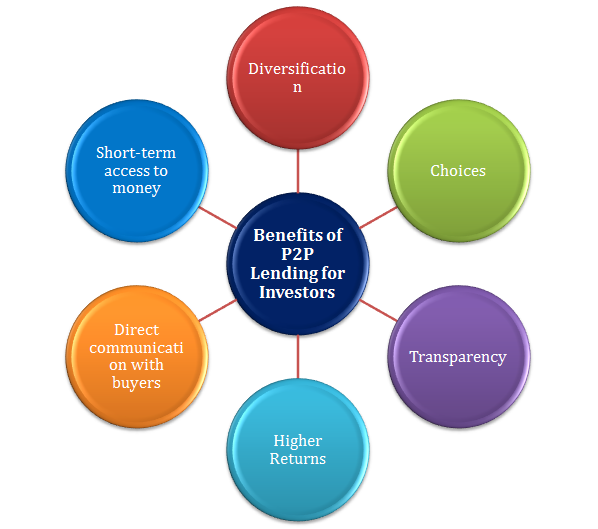


While P2P platforms primarily serve the interests of individuals, they also offer certain benefits to the Nigerian government, albeit indirectly.

Despite their numerous benefits, P2P platforms pose several risks and challenges that both individuals and the government must address.

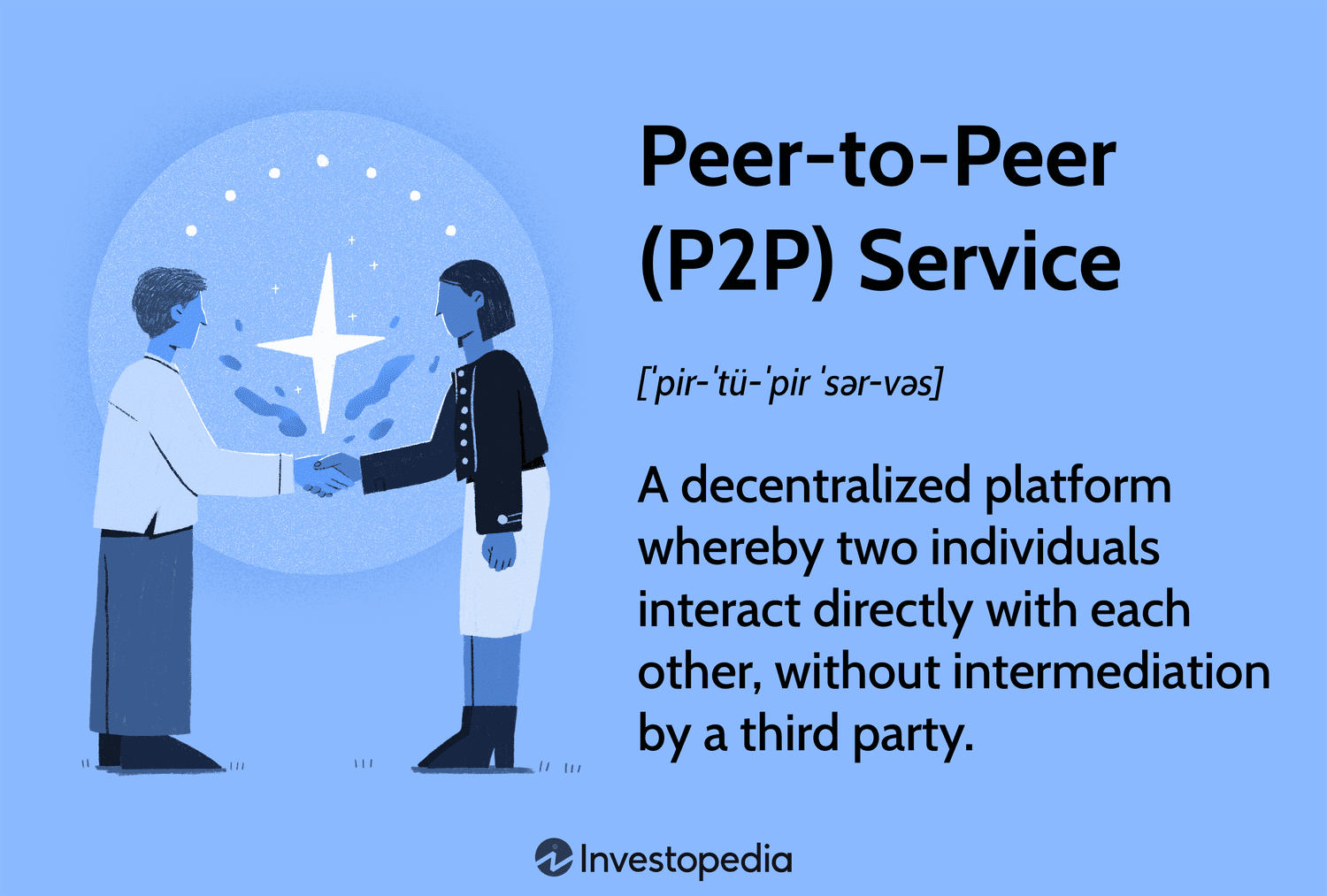
The primary beneficiaries of P2P platforms in Nigeria are individuals and small businesses that gain access to affordable, flexible, and efficient financial services. P2P platforms empower Nigerians by enabling them to:
However, the Nigerian government also benefits indirectly from the proliferation of P2P platforms. These platforms contribute to increased remittance inflows, promote digital financial inclusion, and provide data insights for policy formulation. Nonetheless, the benefits to the government are often secondary and contingent on the successful regulation and formalization of the P2P ecosystem.

The CBN has expressed concerns over the unregulated nature of P2P platforms, particularly in the context of cryptocurrency transactions. In 2021, the CBN banned banks from facilitating cryptocurrency transactions, citing concerns about money laundering and terrorism financing. However, this action drove more Nigerians to P2P platforms, underscoring the resilience of the P2P ecosystem.
To balance the benefits of P2P platforms with the need for regulatory oversight, the Nigerian government is considering the following measures:



The future of P2P platforms in Nigeria is promising, driven by increased internet penetration, growing smartphone adoption, and a tech-savvy population. As the government seeks to balance innovation with regulation, P2P platforms are expected to:

Peer-to-peer (P2P) platforms have emerged as a transformative force in Nigeria’s financial landscape, providing individuals and businesses with greater financial autonomy and access to services. While these platforms primarily benefit the people by offering lower transaction costs, faster processing times, and better exchange rates, they also provide indirect benefits to the government through increased remittance inflows, financial inclusion, and data insights.
However, to fully harness the potential of P2P platforms, Nigeria must strike a delicate balance between promoting innovation and implementing effective regulatory frameworks. As the P2P ecosystem continues to evolve, both the government and the people stand to gain from a well-regulated and transparent financial system.